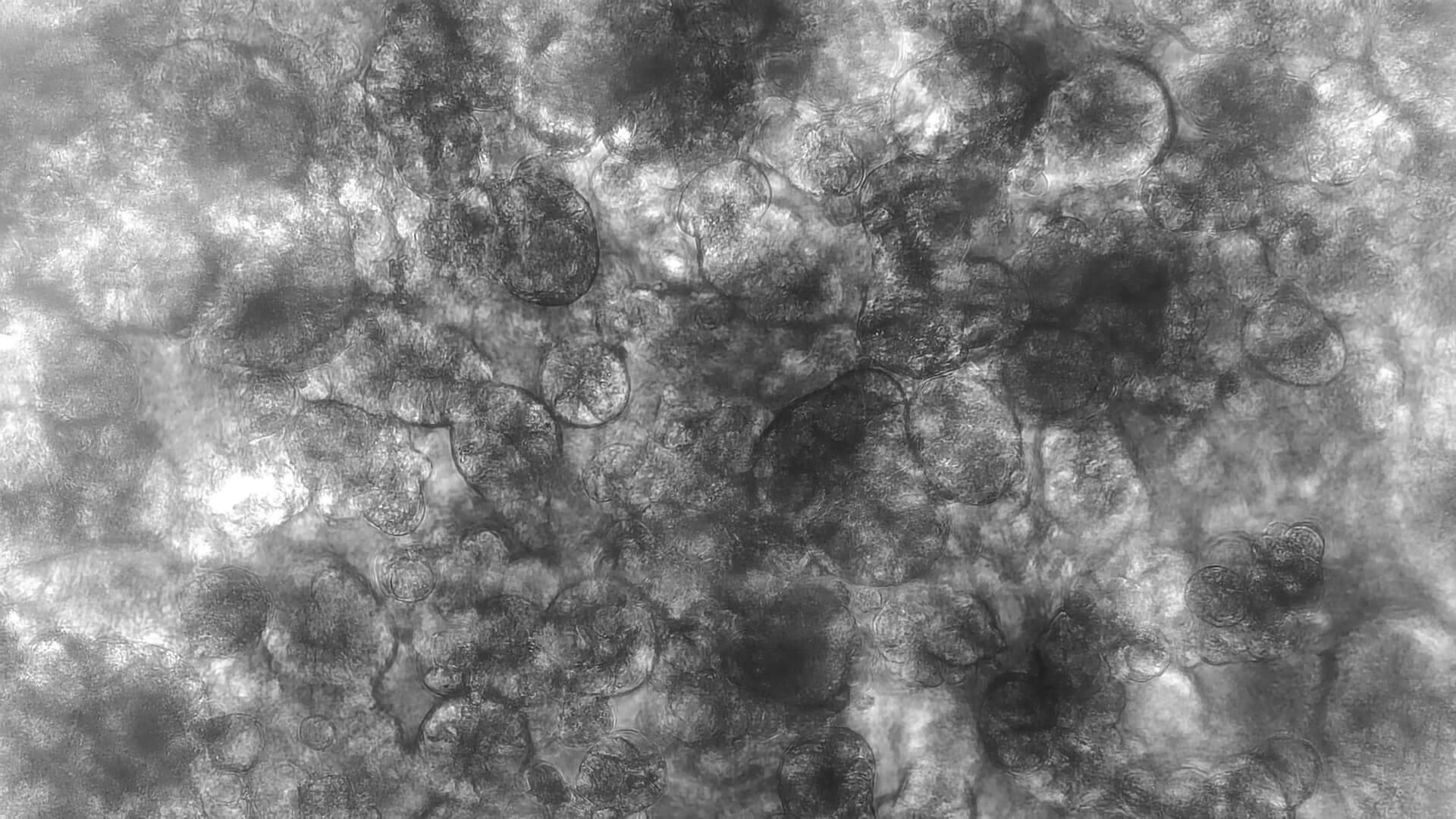
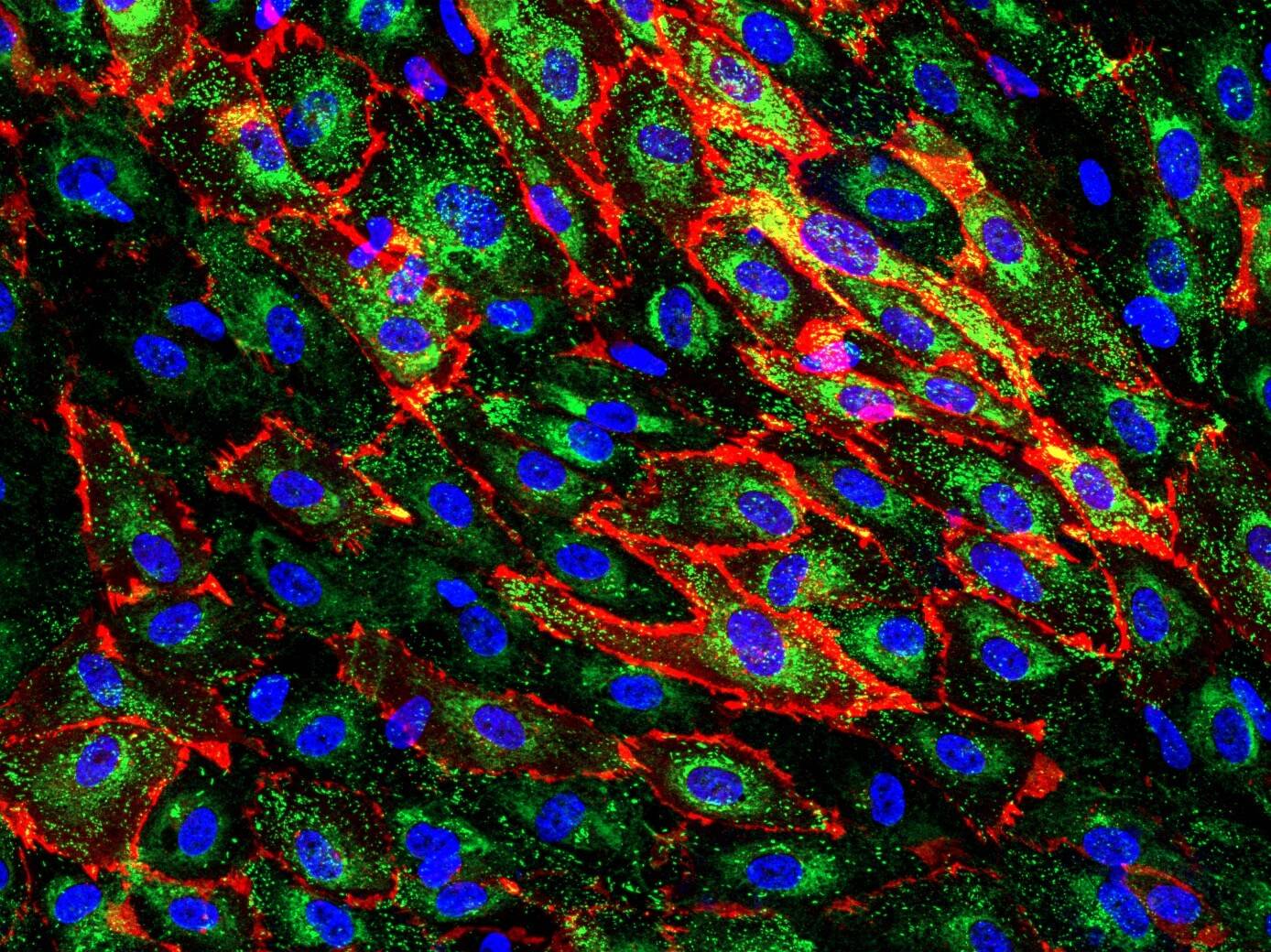
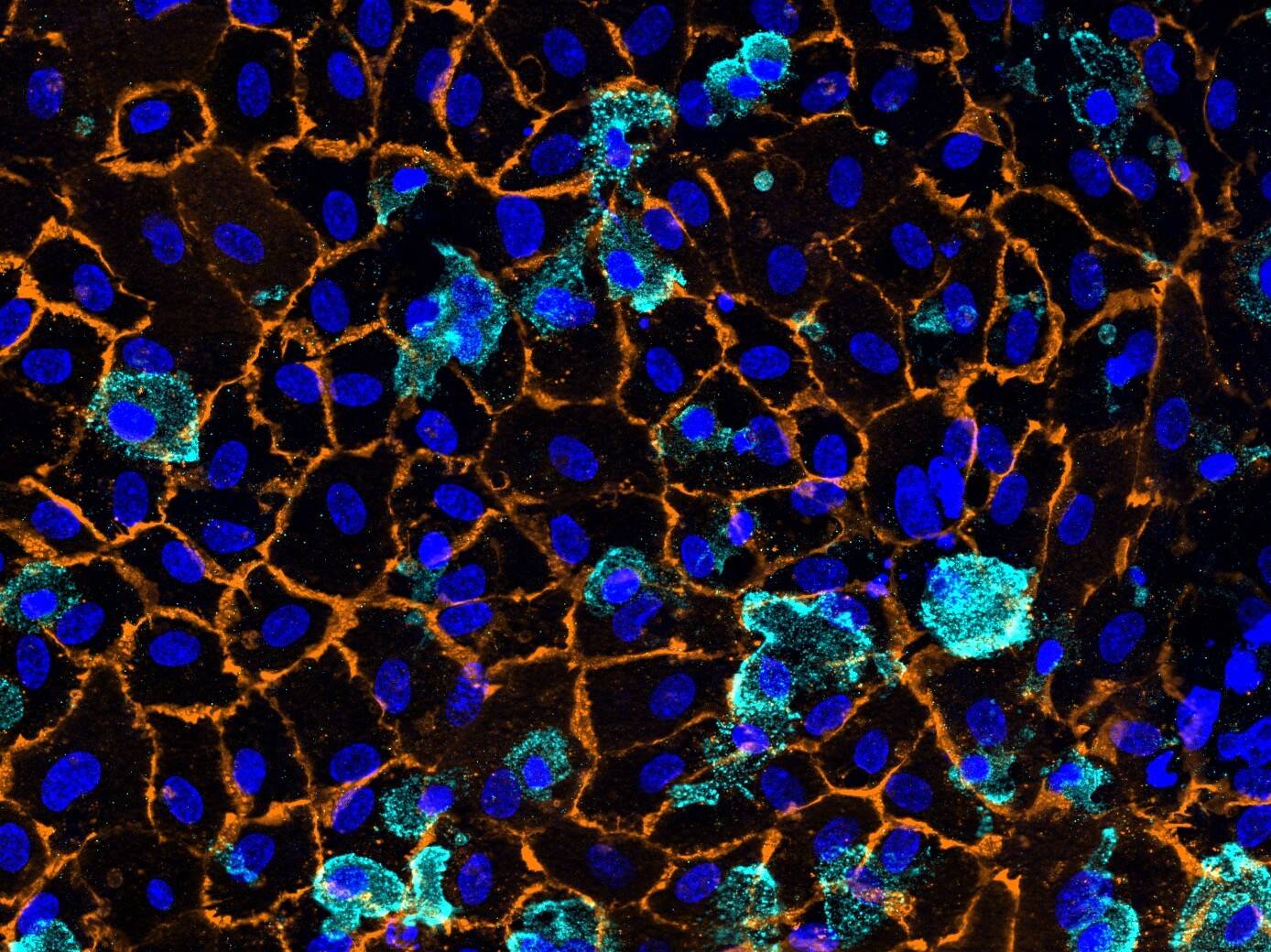
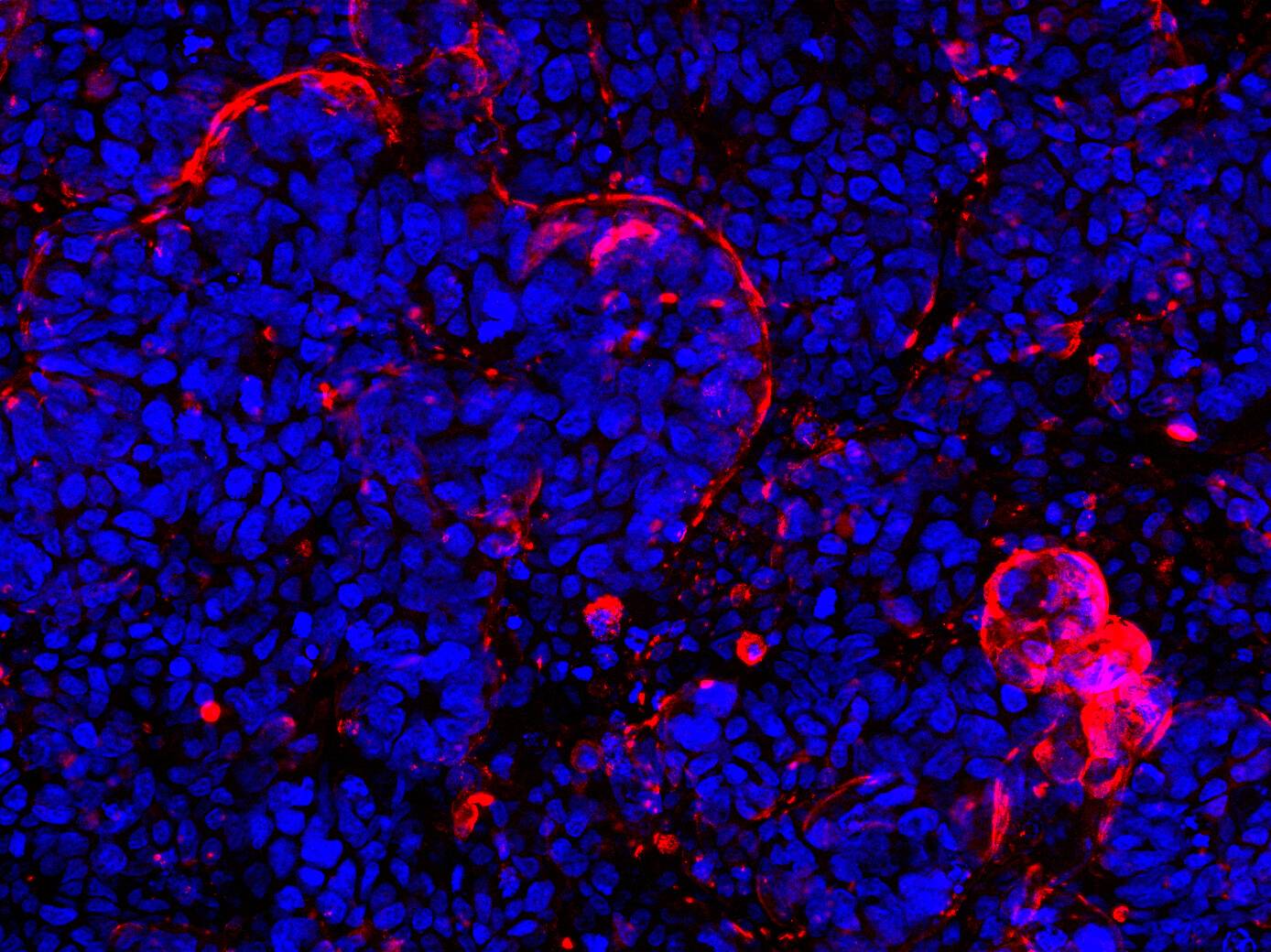
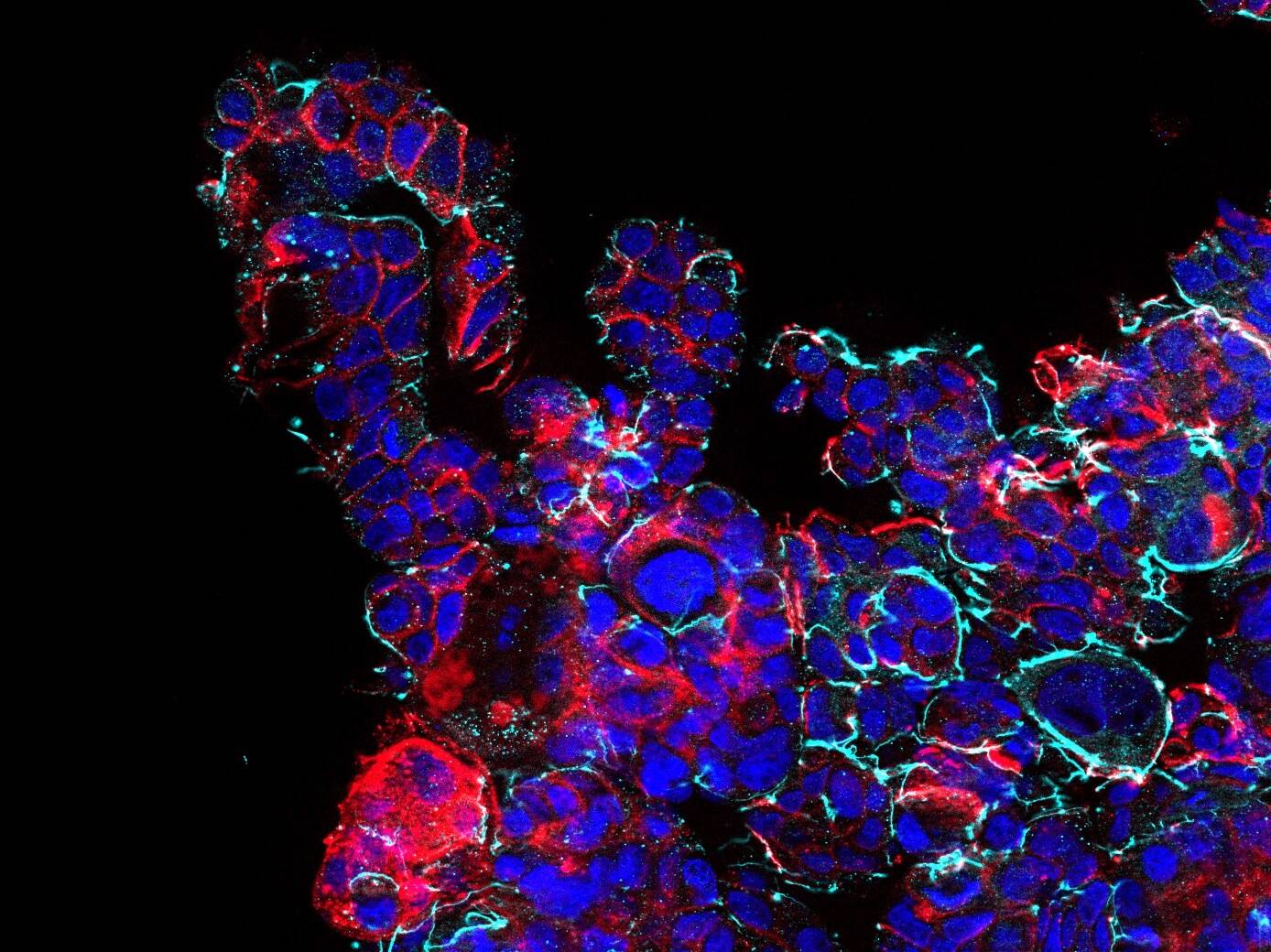
D42 Intestine-on-Chip: Brightfield image showing 14d cultured intestinal tissue structures. Intestinal epithelial cells form a villus-like tissue morphology with crypts inbetween. A three-dimensional tissue outgrowth is essential to enlarge the surface area for nutrient uptake and to provide tissue niches for immune cells and microbial organisms.
The Dynamic42 Intestine-on-Chip can be used to evaluate uptake and mechanistical features of pre-clinical drug candidates, chemicals and food additives or to study inflammatory and infectious diseases.
We use our perfusable Dynamic42 biochip platform to provide an innovative concept to setup in vivo-like microenvironments of the human intestine by reconstructing perfusable villus-like tissue structures.

Specifications
The Dynamic42 Intestine-on-Chip comprises two compartments: a vascular compartment and an intestinal compartment. The vasculature is formed by an endothelial lining and tissue-resident macrophages. The intestinal compartment comprises gut epithelial cells and migrated immune cells such as monocytes or dendritic cells.
The Dynamic42 Intestine-on-Chip can be operated with various cell sources. Please get in contact for further details.

Endothelial Cell

Macrophage
Enterocyte

Goblet Cell

Paneth Cell

Dendritic Cell
Two models can be operated in parallel on one Dynamic42 biochip.
The model has been tested in the following Dynamic42 biochips: BC001 and BC002.
Characteristics
Enhanced marker expression
Intense cell-cell communication
Physiologic biomechanical stimulation via flow
Secretory function
Immunocompetence
The Dynamic42 Intestine-on-Chip can be operated up to 14 days with high vitality, stable barrier function and stable marker expression.
Biomechanical stimulation ensures 3D in vivo-like tissue outgrowth with strong microvilli coverage of cell surfaces.
Applications
- Toxicity profiling
- Uptake / Transport studies
- Host-Microbiome Interaction
- Inflammatory Diseases (IBD)