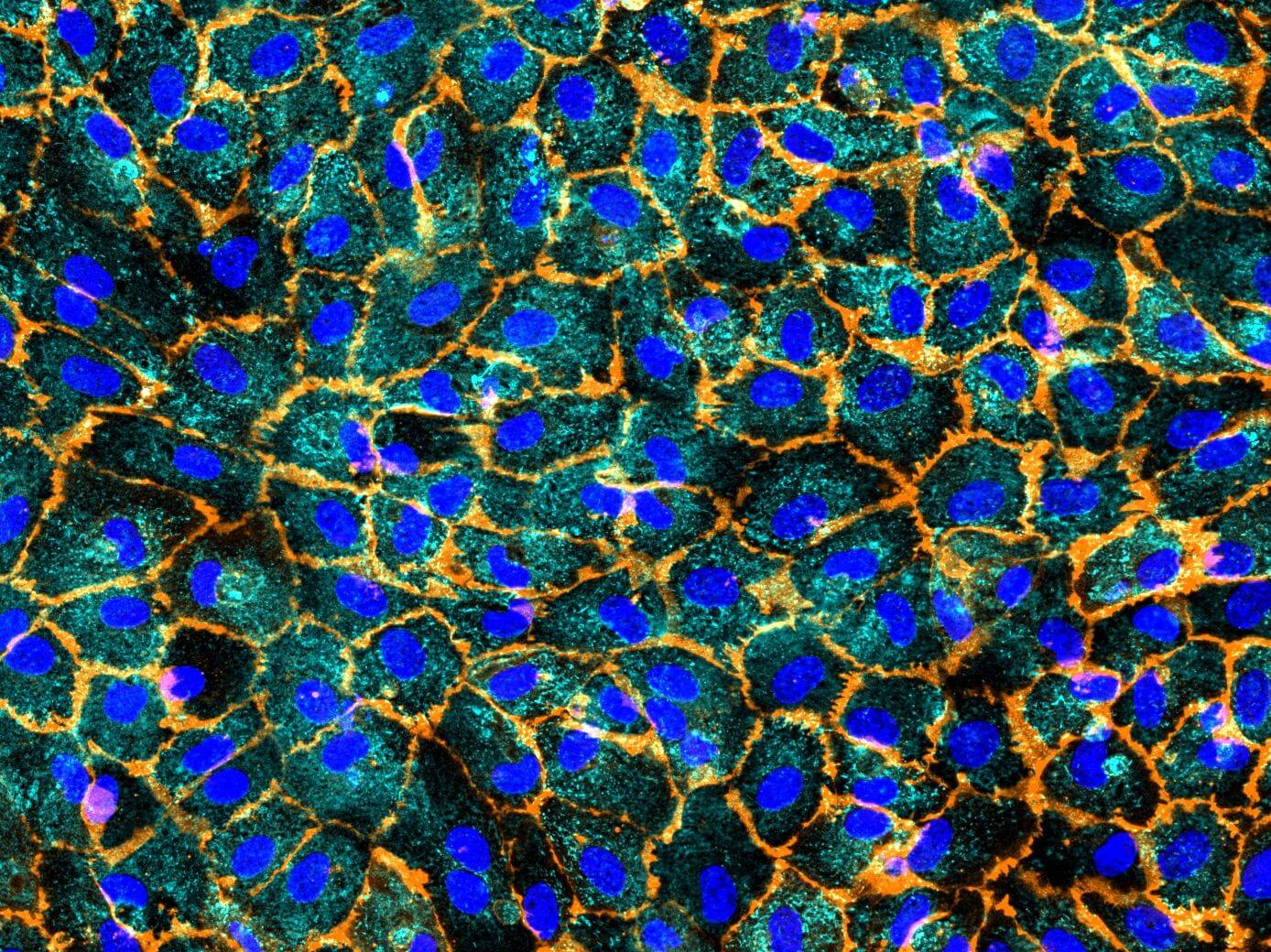
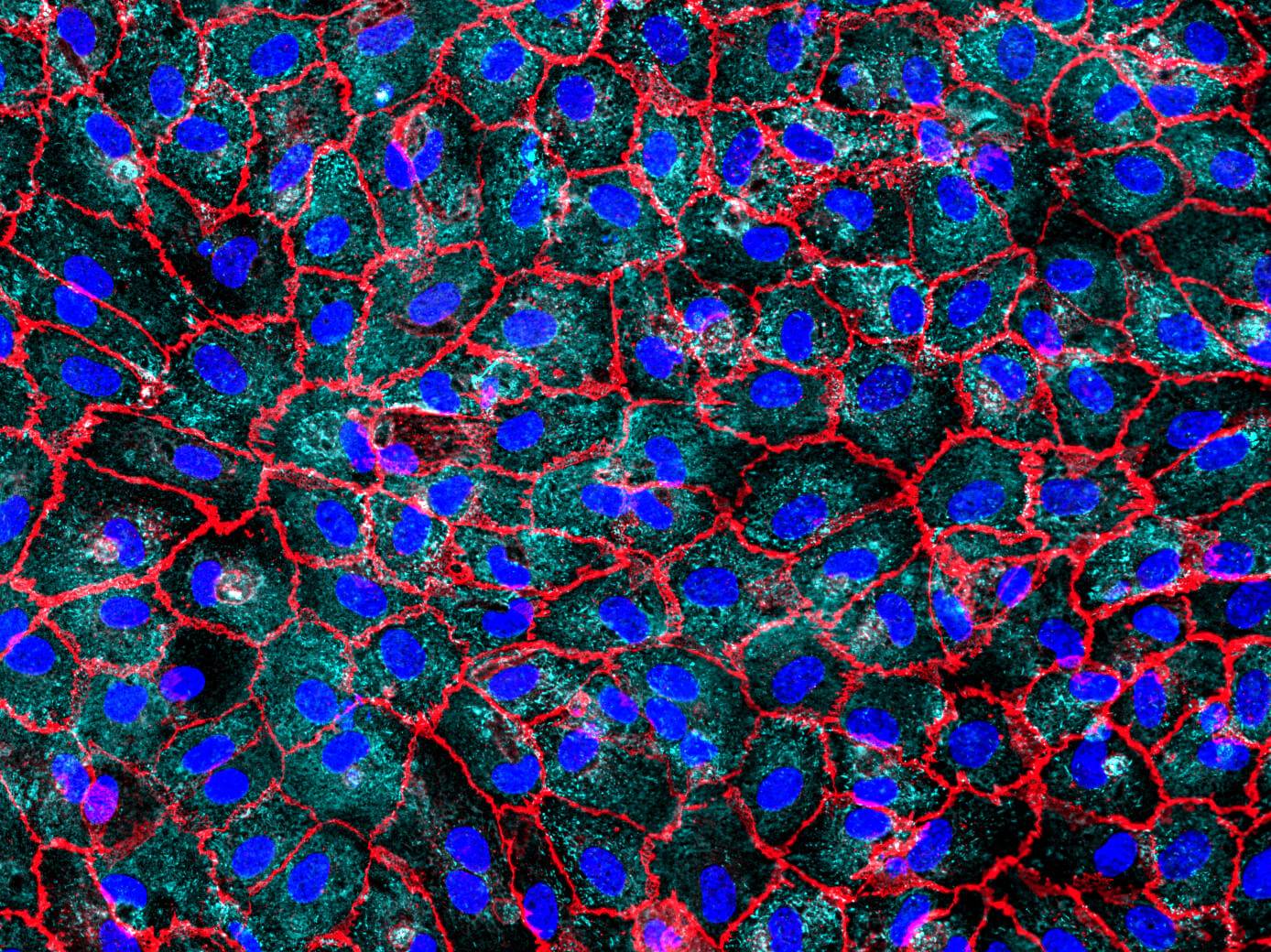
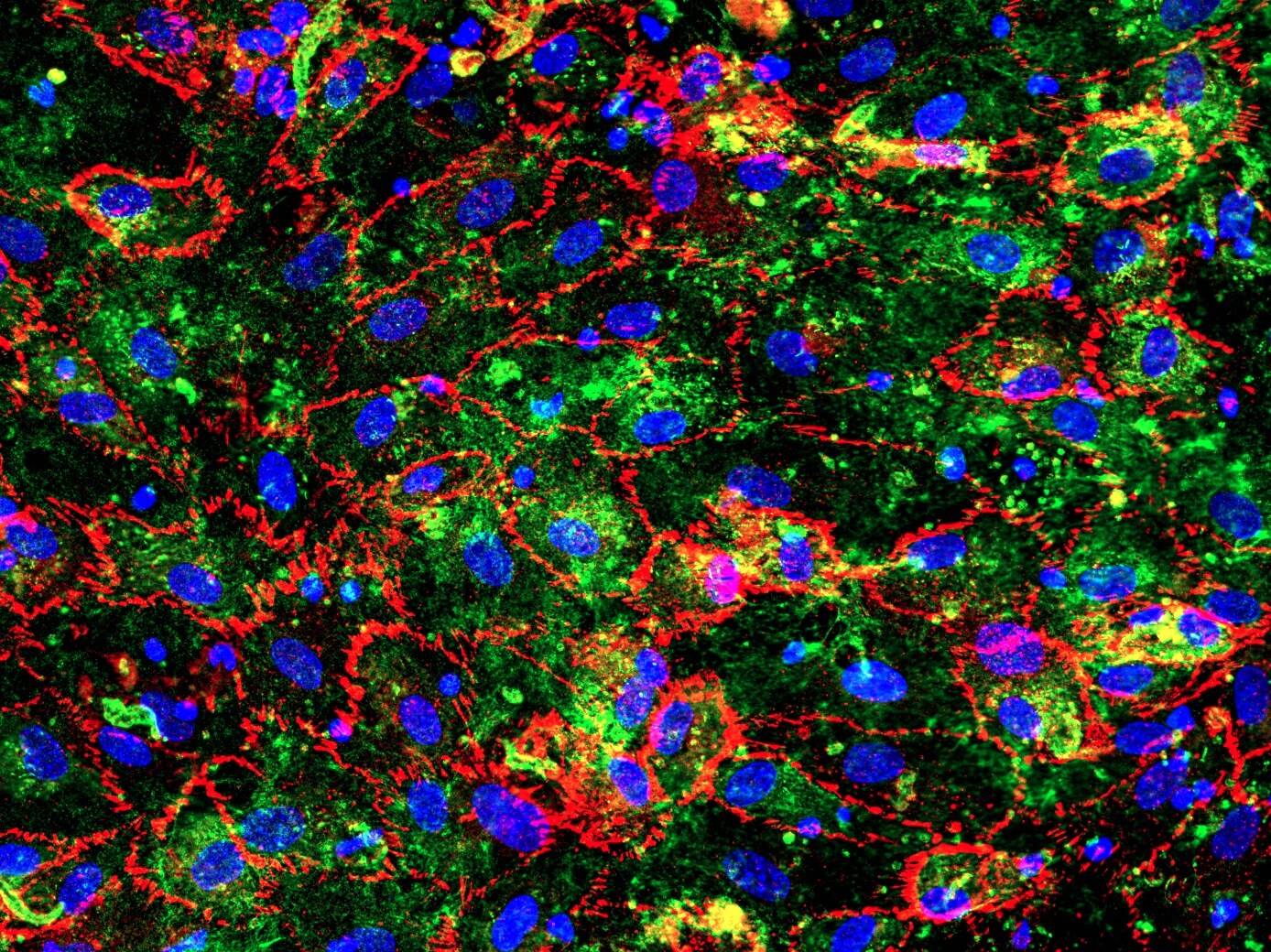
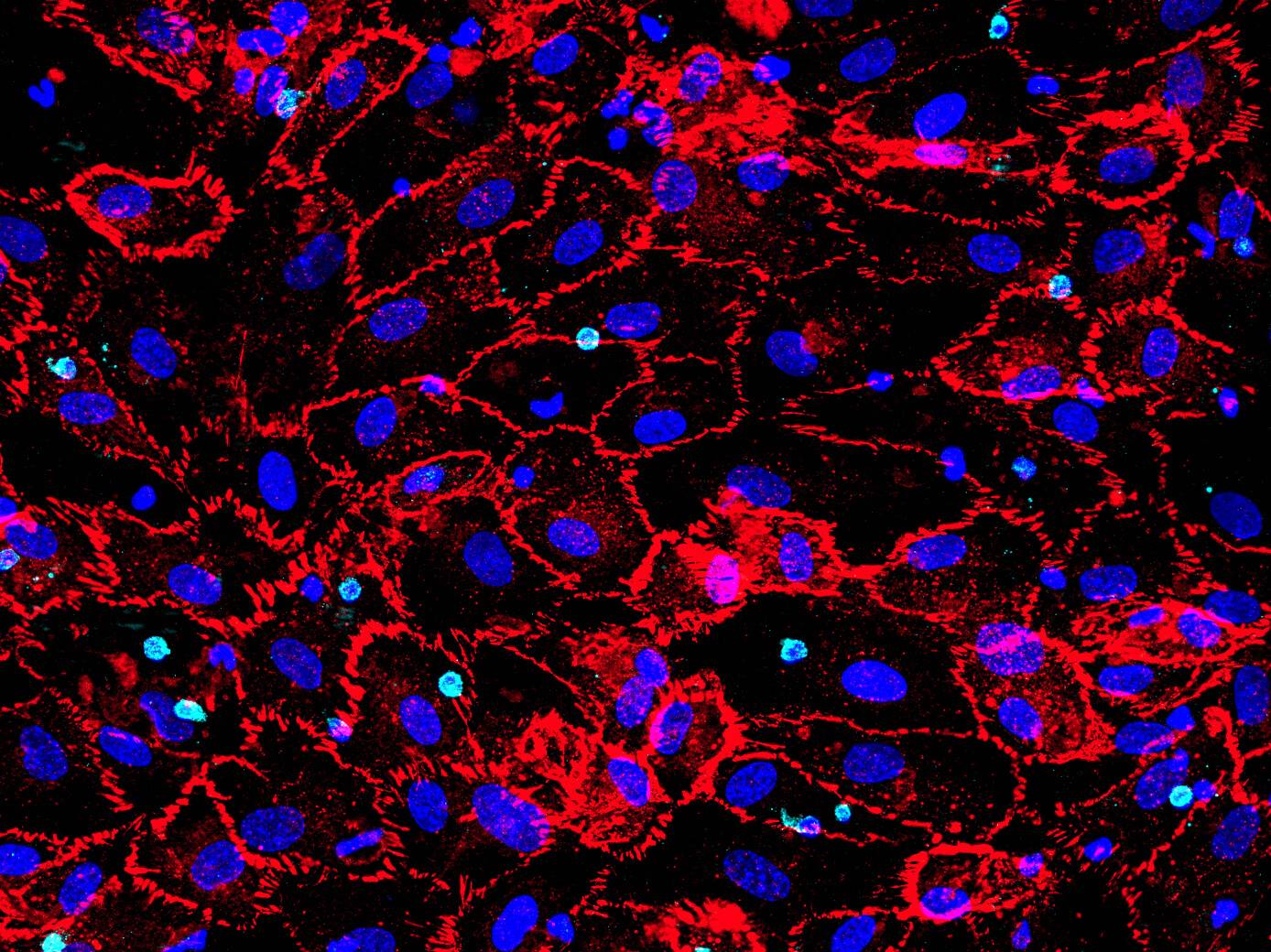
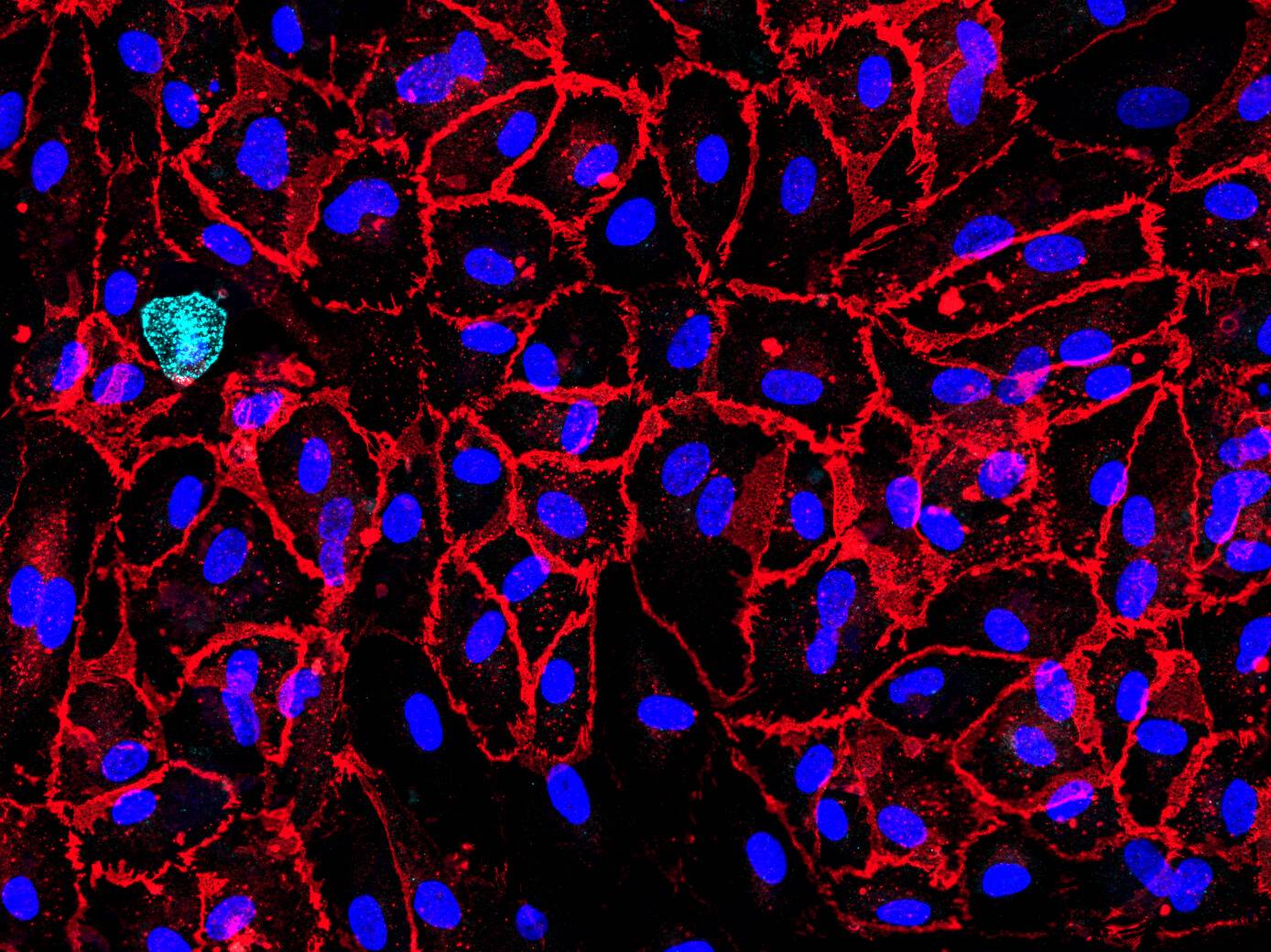
D42 Vasculature-on-Chip: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) display one variant of our model. The cells are stained for von Willebrand factor (vWf) in cyan and CD31 in orange. vWf plays a major role in platelet adhesion and in protective complex formation with factor VIII. CD31 mediates mechano-sensing of biomechanical stimuli and leukocyte adhesion to the vessel wall.
The Dynamic42 Vasculature-on-Chip can be used to evaluate uptake and mechanistical features of pre-clinical drug candidates and chemicals that follow an intravenous delivery. It further qualifies to investigate endothelial interactions with immune cell populations or drug delivery cargos such as nanoparticles and emulsions of various kind.
We use our perfusable Dynamic42 biochip platform to provide an innovative concept to setup in vivo-like microenvironments of the human vasculature by reconstructing perfusable vascular tissue and providing additional biomechanical stimuli. The models qualify to be extended by other vascular cell types such as smooth muscle cells or fibroblasts.

Specifications
The Dynamic42 Vasculature-on-Chip comprises in one compartment endothelial cells and optionally tissue-resident macrophages. It offers the possibility to include circulating immune cell populations. Perfusion and shear rate values are adaptable. Other cell types such as smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts can be included as well to increase complexity.
The Dynamic42 Vasculature-on-Chip can be operated with various cell sources. Please get in contact for further details.


Macrophage
Endothelial Cell
Two models can be operated in parallel on one Dynamic42 biochip.
The model has been tested in the following Dynamic42 biochips: BC001, BC002 and BC005.
Characteristics
Enhanced marker expression
Intense cell-cell communication
Physiologic biomechanical stimulation via flow
Secretory function
Immunocompetence
The Dynamic42 Vasculature-on-Chip can be operated up to 7 days with high vitality, stable barrier function and stable marker expression.
Applications
- Antibody Recycling
- Immune Cell Interactions
- Uptake / Transport studies
- Inflammatory Diseases
- Infectious Diseases